Oct 20, 2024
Following the release of the H1’2024 results by Kenyan insurance firms, the Cytonn Financial Services Research Team undertook an analysis on the financial performance of the listed insurance companies and the key factors that drove the performance of the sector. In this report, we assess the main trends in the sector, and areas that will be crucial for growth and stability going forward, seeking to give a view on which insurance firms are the most attractive and stable for investment. As a result, we shall address the following:
- Insurance Penetration in Kenya,
- Key Themes that Shaped the Insurance Sector in H1’2024,
- Industry Highlights and Challenges,
- Performance of the Listed Insurance Sector in H1’2024, and,
- Conclusion & Outlook of the Insurance Sector.
Section I: Insurance Penetration in Kenya
Insurance uptake in Kenya remains low compared to other key economies with the insurance penetration coming in at 2.4% as of H1’2024, according to the Q4’2023 Insurance Regulatory Authority (IRA) and the Kenya National Bureau of Statistics (KNBS) 2024 Economic Survey. The low penetration rate, which is below the global average of 7.0%, according to the Swiss RE institute, is attributable to the fact that insurance uptake is still seen as a luxury and mostly taken when it is necessary or a regulatory requirement. Notably, Insurance penetration increased by 0.1% points from 2.3% recorded in 2022, showcasing the economic recovery that saw an improved business environment in the country. The chart below shows Kenya’s insurance penetration for the last 13 years:
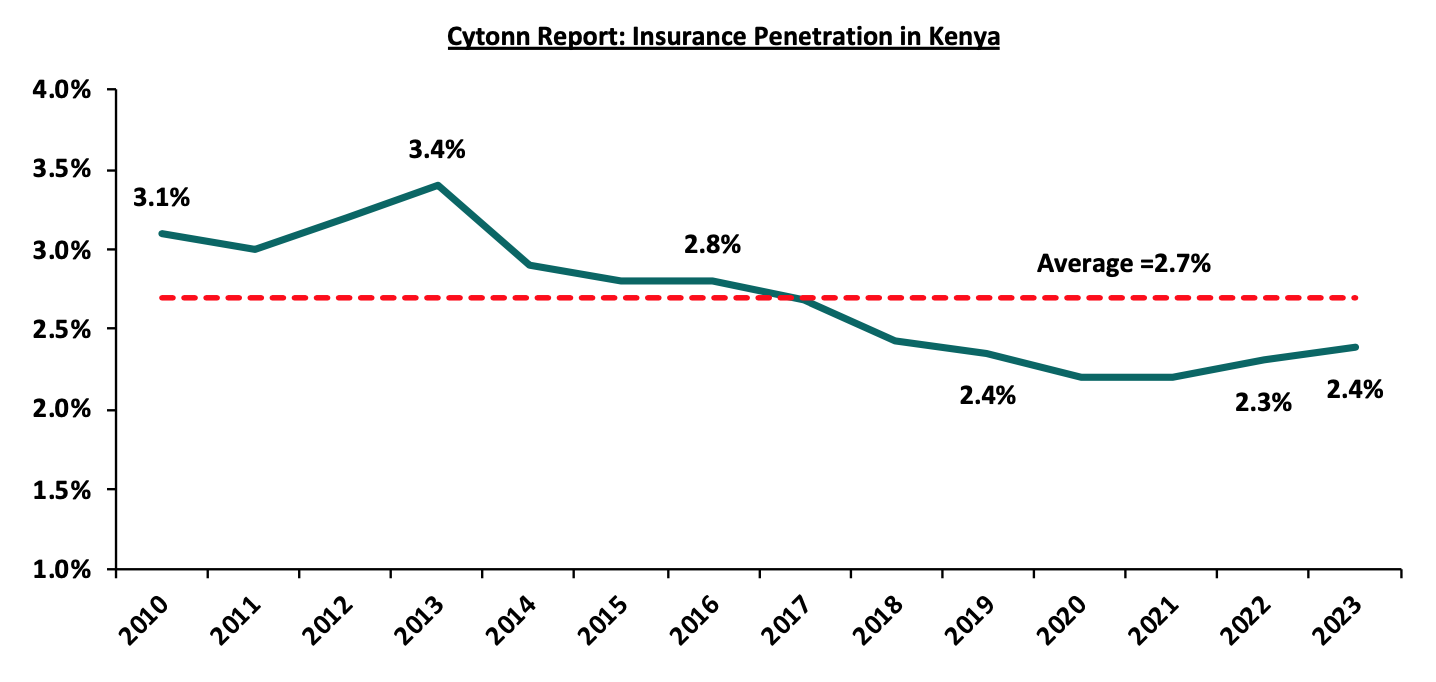
Source: Cytonn Research
The chart below shows the insurance penetration in other economies across Africa:
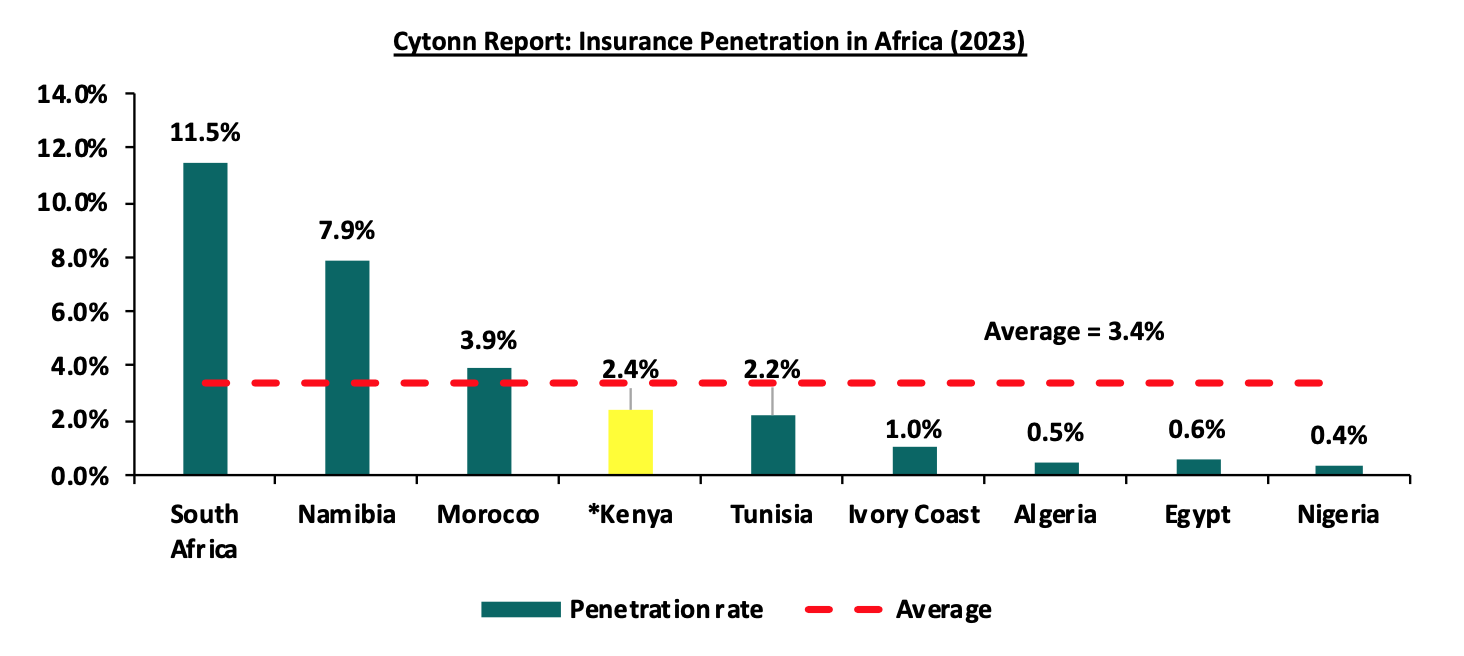
*Data as of 2023
Source: Swiss Re
Insurance penetration in Africa has remained relatively low, averaging 3.4% in 2023, mainly attributable to lower disposable income in the continent and slow growth of alternative distribution channels such as mobile phones to ensure wider reach of insurance products to the masses. South Africa remains the leader in insurance penetration in the continent, owing to a mature and highly competitive market, coupled with strong institutions and a sound regulatory environment.
Section II: Key Themes that Shaped the Insurance Sector in H1’2024
In H1’2024, the country witnessed an improved operating environment on the back of easing inflationary pressures and a strengthening Shilling. Notably, the inflation rate in H1’2024 averaged 5.6%, 2.9% points lower than the 8.5% average in H1’2023, with the Kenyan Shilling having appreciated by 17.2% against the USD in H1’2024. On the other hand, the overall GDP growth rate declined to 4.6% in Q2’2024, from 5.6% recorded in a similar period last year according to the Kenya National Bureau of Statistics. However, according to the Q4’2023 Insurance Regulatory Authority Insurance industry report, the insurance sector showcased resilience recording a 16.7% growth in gross premium to Kshs 361.4 bn in FY’2023, from Kshs 309.8 bn in FY’2022. Insurance claims also increased by 13.3% to Kshs 94.0 bn in FY’2023, from Kshs 82.9 bn in FY’2022.
Notably, the general insurance business contributed 52.9% of the industry’s premium income in FY’2023 compared to 47.1% contribution by long term insurance business in the same period. During the period, the long-term business premiums increased by 20.7% to Kshs 170.0 bn, from Kshs 140.8 bn in 2022 while the general business premiums grew by 13.3% to Kshs 191.3 bn, from Kshs 168.9 bn in 2022. Additionally, motor insurance and medical insurance classes of insurance accounted for 63.5% of the gross premium income under the general insurance business, compared to 64.4% recorded in 2022. As for the long-term insurance business, the major contributors to gross premiums were deposit administration and life assurance classes accounting for 59.8% in FY’2023, compared to the 61.1% contribution by the two classes in FY’2022.
Key highlights from the industry performance:
- Convenience and efficiency through the adoption of alternative channels for both distribution and premium collection such as Bancassurance and improved agency networks,
- Advancement in technology and innovation making it possible to make premium payments and through mobile phones,
- Continued recovery from the ripple effects of the pandemic witnessed in 2020 that saw both individuals and businesses seek insurance uptake to cover their activities, leading to growth in gross premiums which increased by 16.7% to Kshs 361.4 bn in 2023, from Kshs 309.8 bn in 2022 and,
- The sector’s investment income increased by 17.4% to Kshs 69.7 bn in 2023, from Kshs 59.3 bn in 2022, mainly attributable to the 28.1% increase in investment income in the general insurance business to Kshs 15.0 bn, from Kshs 11.7 bn in 2023, coupled with a 14.8% increase in the investment income in the long-term to Kshs 54.7 bn, from Kshs 47.6 bn in 2022.
On valuations, listed insurance companies are trading at a price to book (P/Bv) of 0.5x, lower than listed banks at 0.8x, but both are lower than their 16-year historical averages of 1.3x and 1.6x, for the insurance and banking sectors respectively. These two sectors are attractive for long-term investors supported by the strong economic fundamentals. The chart below shows the price-to-book comparison for Listed Banking and Insurance Sectors:
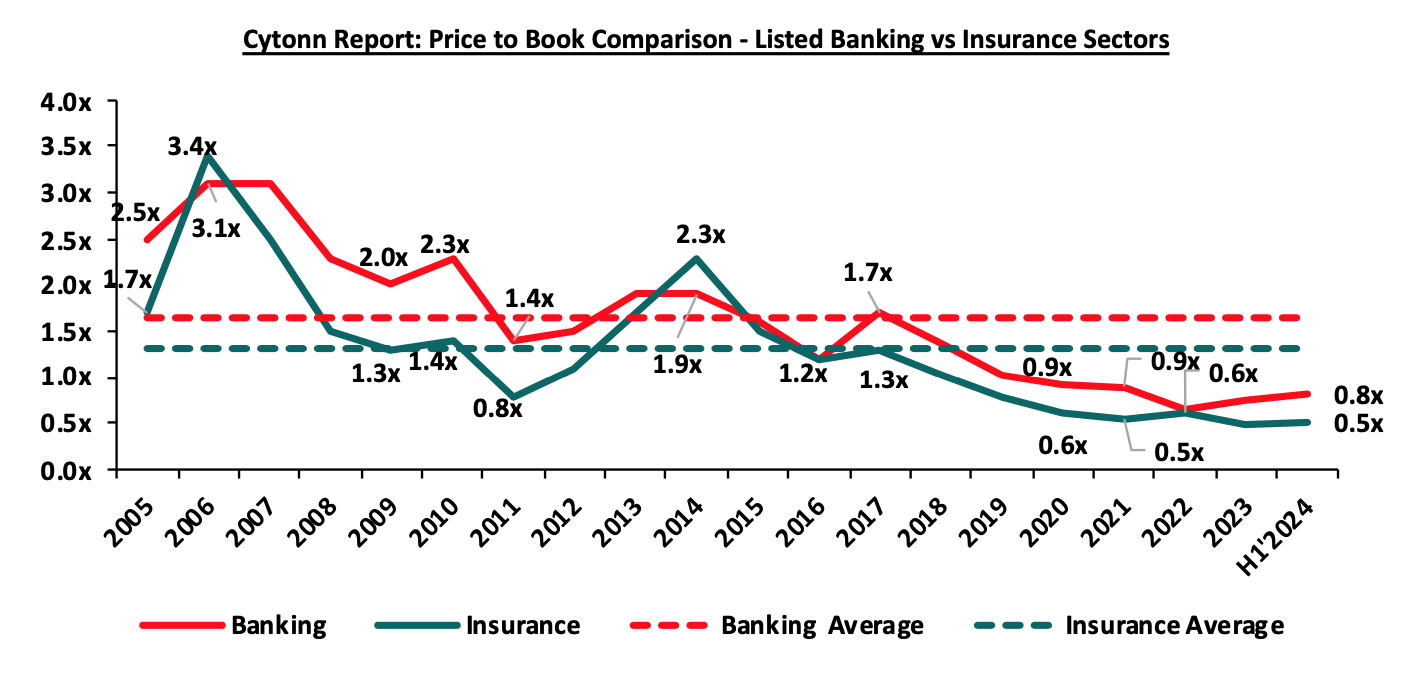
Source: Cytonn Research
The key themes that have continued to drive the insurance sector include:
- Technology and Innovation
Although the industry has been slow in adopting digital trends, the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 saw the adoption of digital distribution of insurance products as a matter of necessity. Consequently, majority of insurance companies continue to take advantage of the available digital channels to drive growth and increase insurance penetration in the country. In April 2024, CIC Group announced the launch of Easy Bima, a digital motor insurance product. This solution allows customers to pay comprehensive motor insurance premiums in equal monthly installments over 12 months, providing flexibility and affordability. The product leverages digital platforms to make insurance more accessible, especially for those who may struggle with upfront premium payments Consumers often term insurance as difficult and complex to understand. This sentiment has been established through various studies carried out to establish reasons for the low uptake of insurance, the latest being the 2021 FinAccess Survey. The survey found that there has been growth in insurance understanding with only 14.3% citing a lack of understanding in 2021 compared to 40.9% in 2016.
- Regulation
To ensure that the sector benefits from a globally competitive financial services sector, the regulator has been working through regulation implementations to address some of the perennial, as well as emerging problems in the sector. The COVID-19 environment proved challenging especially on the regulatory front, as it was a balance between remaining prudent as an underwriter and adhering to the set regulations given the negative effects of the pandemic. Regulations used for the insurance sector in Kenya include the Insurance Act Cap 487 and its accompanying schedule and regulations, the Retirement Benefits Act Cap 197, and The Companies Act. In H1’2024, regulation remained a key aspect affecting the insurance sector and the key themes in the regulatory environment include;
- IFRS 17 - IFRS 9, Financial Instruments was replaced with IFRS 17. The standard establishes the principle for recognition, measurement, presentation, and disclosure of insurance contracts with the objective of ensuring insurance companies provide relevant information that faithfully represents the contracts. However, as a way to protect the insurance industry from the negative effects of the pandemic the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), the international body responsible for setting up financial reporting standards deferred its implementation effective from January 2023 or earlier. The standard, having replaced IFRS 4, is expected to give better information on profitability by providing more insights about the current and future profitability of insurance contracts. Separation of financial and insurance results in the income statement will allow for better analysis of core performance for the entities and allow for better comparability of insurance companies, and,
- Risk-Based Supervision - IRA has been implementing risk-based supervision through guidelines that require insurers to maintain a capital adequacy ratio of at least 200.0% of the minimum capital. The regulation requires insurers to monitor the capital adequacy and solvency margins on a quarterly basis, with the main objective being to safeguard the insurer’s ability to continue as a going concern and provide shareholders with adequate returns. We expect more mergers within the industry as smaller companies struggle to meet the minimum capital adequacy ratios. We also expect insurance companies to adopt prudential practices in managing and taking on risk and reduction of premium undercutting in the industry as insurers will now have to price risk appropriately.
- Capital Raising and Share Purchase
The move to a risk-based capital adequacy framework presented opportunities for capital raising initiatives mostly by the small players in the sector to shore up their capital and meet compliance measures. With the new capital adequacy assessment framework, capital is likely to be critical to ensuring stability and solvency of the sector to ensure the businesses are a going concern. In May 2022, Sanlam Limited, a South African financial services group listed on the Johannesburg Stock Exchange, announced that it had entered into a definitive Joint Venture agreement for a term of 10 years with Allianz SE, with the aim to leverage the two entities footprints in Africa and create a leading Pan-African financial services group, with an estimated equity value of Kshs 243.7 bn. Key to note, Sanlam Limited, indirectly owns 100.0% of Hubris Holdings Limited, which is the majority shareholder in Sanlam Kenya Plc, a listed insurance and financial services entity on the Nairobi Stock Exchange. The initial shareholding split of the Joint Venture was announced to be 60:40, Sanlam Limited to Allianz respectively, with the effective date of the proposed transaction being within 12-15 months of the announcement, subject to relevant approvals. However, given the length of the Agreement, we expect that the Joint Venture will provide for Sanlam Kenya Plc, Allianz General Insurance Kenya, and Jubilee General Insurance (which Allianz owns the majority stake in – 66.0%), to combine operations to grow their market share, asset base and bottom lines.
Section III: Industry Highlights and Challenges
The insurance industry has experienced steady growth over the last decade, as a result, we anticipate sustained moderate growth on the back of an improving economy and subsequent rise in insurance premiums, which will strengthen the sector's ability to sustain profitability.
On the regulatory front, the rejected Finance Bill 2024 included provisions that sought to expand taxes on insurance premiums and extend VAT to certain insurance services. These included a new 2.5% tax on the value of motor vehicles, payable when issuing insurance cover and limiting VAT exemptions to insurance and reinsurance premiums only, subjecting other related services to the standard VAT rate of 16.0%. These measures were aimed at increasing government revenue but were met with opposition from industry stakeholders, including the Association of Kenya Insurers (AKI) due to concerns over increased insurance costs. The rejection of the Finance Bill has provided a temporary reprieve for the insurance sector, though discussions on balancing fiscal policy and market growth continue to shape the regulatory landscape.
Industry Challenges:
- Insurance fraud: Insurance Fraud is an intentional deceit performed by an applicant or policyholder for financial advantage. In recent years, there has been an upsurge in fraudulent claims, particularly in medical and motor insurance, with estimates indicating that one in every five medical claims are fraudulent. This is mainly through exaggerating medical costs and hospitals by making patients undergo unnecessary tests. Notably, in 2023, 206 fraud instances were reported, with 56 cases reported in Q4’2023 alone. Fraudsters also collude with hospitals to make false claims, and fake surgeries and treatments, while healthcare providers overcharge insured patients. To combat fraud, the sector has adopted the usage of blockchain and artificial intelligence,
- Insolvency: A major challenge facing the insurance industry is the financial instability and insolvency of key players, as evidenced by recent cases like Xplico Insurance, Invesco Assurance and Resolution Insurance. These companies have been placed under statutory management and provisional liquidation by the Insurance Regulatory Authority (IRA). The issues stem from prolonged financial difficulties, boardroom conflicts, and eroding market share, particularly in loss-making segments like Public Service Vehicle (PSV) insurance. The collapse of these insurers affects customer trust, disrupts the industry’s stability, and forces policyholders to seek alternative coverage. The industry must address governance, risk management, and liquidity issues to restore stability and consumer confidence,
- Declining consumer confidence in the insurance industry: In 2023, IRA received 440 complaints from policyholders and beneficiaries lodged against insurers, the general insurance accounting for the majority of the complaints at 77.5%, while long-term insurers recorded 22.5%. The complaints range from insurance companies failing to settle claims and constant haggling over terms of insurance,
- High Market competition: Despite low insurance penetration in the country, the sector is served by 57 insurance companies offering the same products. Some insurers have resorted to shady tactics in the fight for market dominance, such as premium undercutting, which involves offering clients implausibly low premiums to gain a competitive advantage and protect their market share. This is a significant factor in the industry's underwriting losses. Plans to hire a consultant to review industry pricing in March 2021 were retaliated against by the regulator, but the plans are still in the works. However, this is against a background of weak insurance uptake, which could be made worse by higher premium prices. Industry participants have debated pricing, and,
- Regulation compliance: Due to laws on capital requirements, smaller insurance businesses have found it challenging to operate without raising capital or combining to expand their capital base. Additionally, the implementation of IFRS 17, is expensive since accounting and actuarial systems need to be updated and realigned.
Section IV: Performance of the Listed Insurance Sector in H1’2024
The table below highlights the performance of the listed insurance sector, showing the performance using several metrics, and the key take-outs of the performance.
|
Cytonn Report: Listed Insurance Companies H1’2024 Earnings and Growth Metrics |
||||||||
|
Insurance |
Core EPS Growth |
Net Premium growth |
Claims growth |
Loss Ratio |
Expense Ratio |
Combined Ratio |
ROaE |
ROaA |
|
Liberty |
196.7% |
403.1% |
(295.6%) |
70.6% |
104.4% |
175.0% |
6.7% |
1.4% |
|
Sanlam |
164.1% |
28.4% |
15.6% |
89.6% |
74.3% |
163.9% |
28.0% |
0.8% |
|
Jubilee Insurance |
22.7% |
28.4% |
15.6% |
89.6% |
74.3% |
163.9% |
4.8% |
1.3% |
|
Britam |
22.6% |
7.4% |
14.6% |
76.2% |
69.1% |
145.3% |
8.0% |
2.0% |
|
CIC |
0.6% |
(0.4%) |
(6.9%) |
81.0% |
29.1% |
110.1% |
7.9% |
1.3% |
|
*H1'2024 Weighted Average |
39.6% |
51.7% |
(18.2%) |
81.1% |
68.2% |
149.4% |
7.3% |
1.6% |
|
**H1'2023 Weighted Average |
(235.5%) |
6.7% |
(3.6%) |
57.8% |
56.4% |
114.2% |
3.2% |
1.0% |
|
*Market cap weighted as at 18/10/2024 |
||||||||
|
**Market cap weighted as at 27/10/2023 |
||||||||
The key take-outs from the above table include;
- Core EPS growth recorded a weighted growth of 39.6%, significantly higher compared to the weighted decline of 235.5%, in H1’2023. The improved growth in earnings was attributable to increased premiums during the period following continued recovery by the sector from the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, coupled with higher yields from government papers,
- The premiums grew at a significantly quicker pace of 51.7% in H1’2024, compared to a growth of 6.7% in H1’2023, while claims declined at a higher rate of 18.2% in H1’2024, from the 3.6% decline recorded in H1’2023 on a weighted average basis,
- The loss ratio across the sector increased to 81.1% in H1’2024 from 57.8% in H1’2023,
- The expense ratio increased to 68.1% in H1’2024, from 56.4% in H1’2023, owing to an increase in net premiums,
- The insurance core business still remains unprofitable, with a combined ratio of 149.4% as of H1’2024, higher than the 114.2% in H1’2023, and,
- On average, the insurance sector delivered a Return on Average Equity (ROaE) of 7.3%, an increase from a weighted Return on Average Equity of 3.2% in H1’2023.
Based on the Cytonn H1’2024 Insurance Report, we ranked insurance firms from a franchise value and from a future growth opportunity perspective with the former getting a weight of 40.0% and the latter a weight of 60.0%.
For the franchise value ranking, we included the earnings and growth metrics as well as the operating metrics shown in the table below in order to carry out a comprehensive review:
|
Cytonn Report: Listed Insurance Companies H1’2024 Franchise Value Score |
||||||
|
Insurance Co. |
Loss Ratio |
Expense Ratio |
Combined Ratio |
Tangible Common Ratio |
Franchise Value Score |
Ranking |
|
Britam |
76.2% |
69.1% |
145.3% |
13.1% |
13 |
1 |
|
Liberty |
70.6% |
104.4% |
175.0% |
18.0% |
15 |
2 |
|
CIC |
81.0% |
29.1% |
110.1% |
13.9% |
17 |
3 |
|
Jubilee Insurance |
89.6% |
74.3% |
163.9% |
25.8% |
21 |
4 |
|
Sanlam |
89.6% |
74.3% |
163.9% |
1.5% |
24 |
5 |
|
*H1'2024 Weighted Average |
81.1% |
68.2% |
149.4% |
17.6% |
|
|
The Intrinsic Valuation is computed through a combination of valuation techniques, with a weighting of 40.0% on Discounted Cash-flow Methods, 35.0% on Residual Income, and 25.0% on Relative Valuation. The overall H1’2023 ranking is as shown in the table below:
|
Cytonn Report: Listed Insurance Companies H1’2024 Comprehensive Ranking |
|||||
|
Bank |
Franchise Value Score |
Intrinsic Value Score |
Weighted Score |
H1’2024 Ranking |
H1’2023 Ranking |
|
Jubilee Holdings |
4 |
1 |
2.2 |
1 |
2 |
|
Britam Holdings |
1 |
4 |
2.8 |
2 |
5 |
|
CIC Group |
3 |
3 |
3.0 |
3 |
1 |
|
Sanlam Kenya |
5 |
2 |
3.2 |
4 |
4 |
|
Liberty Holdings |
2 |
5 |
3.8 |
5 |
3 |
Major Changes from the H1’2023 Ranking are;
- Jubilee Holdings improved to position 1 in H1’2024 mainly due to the strong intrinsic scores and an improvement in franchise score in H1’2024, driven by a decrease in loss ratio to 89.6% in H1’2024, from 114.5% recorded in H1’2023
- Britam Holdings improved to position 2 in H1’2024 driven by an improvement in franchise score, attributable to the improvement in return on average assets to 2.0%, from 1.0%, coupled with a decline in expense ratio to 69.1% in H1’2024 from 71.4% recorded in H1’2023,
- CIC Group declined to position 3 in H1’2024, mainly due to declines in franchise scores in H1’2024, driven by the deterioration in the net premium growth to a decline of 0.4%, from the 19.9% growth recorded in H1’2023, and,
- Liberty Holdings declined to position 5 in H1’2024 driven by a deterioration in franchise score, attributable to the increase in the expense ratio to 104.4%, from a 71.2% recorded in H1’2023.
Section V: Conclusion & Outlook of the Insurance Sector
With the recent improvements in the Kenyan economy, the insurance industry is poised for a more positive outlook. As inflationary pressures continue to ease and the currency stabilizes, households are expected to have higher disposable income, which can help boost insurance penetration rates. While the industry continues to face challenges, it also benefits from ongoing digital transformation and innovation, which began to accelerate during the pandemic. Regulatory improvements and customer-centric approaches remain key areas of focus. The improved economic conditions provide a more stable environment for insurers to grow, with opportunities to enhance product offerings, improve customer engagement, and tailor policies that cater to the shifting financial capabilities of consumers.
The insurance sector should build on the following strategies to sustain growth and capitalize on the economic upturn:
- Partnerships and alternative distribution channels: We anticipate that underwriters will continue to form alliances and offer additional distribution channels in the future. This can be accomplished by collaborating with other financial services providers, such as fund managers who have moved into delivering insurance-linked products, in addition to the present bancassurance connection with banks. The insurance business can also use the penetration of bank products to promote their own products. For instance, in July 2024, NCBA Group announced the completion of a 100.0% acquisition of AIG Kenya Insurance Company (AIG Kenya). This move allows NCBA to leverage its physical and digital platforms to boost insurance penetration in Kenya and the wider East African region. This acquisition aligns with the broader trend of partnerships and alternative distribution channels, as NCBA’s collaboration with AIG Kenya demonstrates how banks and insurance providers can work together to broaden access to insurance products,
- Regional Diversification - As insurers look to expand their portfolios and mitigate risks, entering new markets can provide growth opportunities and help spread exposure across multiple economies. This strategy allows companies to tap into underpenetrated regions, improving overall revenue streams and reducing dependence on local markets. By entering emerging and underserved markets, insurers can gain access to new customer bases, diversify their product offerings, and strengthen their positions across Africa and beyond. For instance, in June 2024, Britam announced its plans to expand into the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) as part of its five-year strategy to grow regionally. This expansion builds on its success in international markets, which contributed 29.0% of its total insurance revenue in 2023. With strong performance driving a 65.0% increase in profit before tax, Britam continues to focus on growth and customer-centric transformation,
- Regulations - To ensure the sector's solvency and sustainability, we anticipate more regulation from the regulatory body and other international stakeholders. Insurers must modify their insurance contract recognition techniques in advance of the implementation of IFRS 17. The regulator's quest for the targeted capital adequacy levels will almost certainly result in further consolidations as insurers struggle to achieve the capital requirements, particularly for small firms. Furthermore, regulators, governments, and policymakers are working harder to make Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards a requirement in the insurance industry,
- Innovation: To aid portfolio expansion and growth, insurers must harness the digital insurance solutions at their disposal in order to improve internal efficiency and accelerate time to market. As such, we anticipate cooperation between insurers and InsurTechs. For instance, in July 2024, the Insurance Regulatory Authority (IRA) launched The BimaLab Africa Accelerator Programme 2024. This program aims to offer hands-on support to startups developing insurance solutions for underserved, climate-vulnerable communities. The accelerator fosters innovation by connecting investors, building capacity, and unlocking capital, creating a strong ecosystem for InsurTechs to collaborate with traditional insurers in developing tailored solutions for these communities,
- Investment diversification - To improve earnings and reduce losses, underwriters should focus more on investment diversification through routes such as pension plans, unit trusts, fund management, and investment advisories. As indicated by rising combined ratios, insurers have suffered losses in their core business, with increases in underwriting expenditures and claims exceeding increases in premiums. In addition, we anticipate insurers will continue to investigate non-traditional asset types such as infrastructure, and,
- Insurance awareness campaigns – Low insurance penetration is significantly impacted by the persistent information gap about insurance products and their significance. Insurance is still largely assumed to be regulatory compliance rather than a necessity. The regulators, insurers, and other stakeholders should enhance insurance awareness campaigns to increase understanding of insurance products. According to a survey commissioned by the Association of Kenya Insurers (AKI), the second largest contributor to low insurance uptake at 27.0% is a lack of knowledge of the various insurance products and their benefits. As such, there is a lot of headroom for insurers to educate, repackage, and tailor their products to different potential clients.
For more information, please read our H1’2024 Listed Insurance Sector full report.
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this publication are those of the writers where particulars are not warranted. This publication is meant for general information only and is not a warranty, representation, advice, or solicitation of any nature. Readers are advised in all circumstances to seek the advice of a registered investment advisory.

