Aug 16, 2020
Retirement Planning is not something we can start later because later is when we retire. In Cytonn Weekly #08/2020, we discussed the importance of financial planning, the various considerations based on one’s own uniqueness, needs and preferences, and some of the investment avenues available. This week, we focus on: how to plan your finances in preparation for retirement given its inevitability, various types of pension schemes and where pension schemes invest.
To further explain retirement, we look at the topic in five sections as follows:
- Introduction: Pensions Industry in Kenya and Benefits of Saving in a Retirement Benefits Scheme,
- Types of Retirement Benefits Schemes,
- Pension Historical Performance (Segregated vs Guaranteed) and Asset Allocation,
- Impact of COVID-19 on Retirement Benefits Scheme,
- Access To Your Pension Savings, and,
- Conclusion – Factors To Consider Before Joining a Pension Scheme
Section 1: Introduction: Pensions Industry in Kenya and Benefits of Saving in a Retirement Benefits Scheme
In Kenya, The Retirement Benefits Authority (“RBA”) is the governing body established under the terms of the Retirement Benefits Act 1997 tasked with regulating and supervising the establishment, management and promotion of retirement benefits schemes. The Authority’s mandate also includes:
- Protecting the interest of members and sponsors of retirement benefits schemes
- Promoting the development of the retirement benefits sector
- Implementing all government policies relating to the sector
- Advising the CS National Treasury on the national policy to be followed with regard to the retirement benefits industry
The RBA’s mandate covers all private and government parastatal pension schemes. The civil service pension scheme and the Teachers Services Commission pension scheme is governed by the pensions department under the Ministry of National Treasury.
The pensions industry refers to the economic sector comprising of retirement benefits schemes, the assets these schemes control and relevant regulations affecting the schemes’ operations. The industry has witnessed significant growth with the number of registered members increasing from 0.7 mn and assets under management worth Kshs 0.42 tn shillings in 2010 to 3.0 mn members and assets worth Kshs 1.32 tn as of December 2019, according to the Kenya National Bureau of Statistics (KNBS) FinAccess Report 2019.
Despite the aforementioned growth in the industry, about 80% of the working population in Kenya are not members of any pension scheme. Below we look at the reasons why one should join a pension scheme:
- Income Replacement – Retirement savings ensure that your income stream does not stop even when you stop working. After retirement, many experience a decline in the amount and stability of income relative to their productive years. Retirement savings ensures that this decline is manageable or is non-existent and enables you to be able to live the lifestyle you desire even after retirement,
- Compounded and Tax-free interest – Savings in a pension scheme earns compounded interest which means that your money grows faster as even the interest earned is reinvested and grows. Additionally, retirement schemes are tax exempt meaning that the schemes have more to reinvest,
- Tax-exempt contributions – Pension contributions enjoy a monthly tax relief of up to Kshs 20,000 or 30% of your salary whichever is less – this lessens the total PAYE deducted from your earnings
- Avoid old age poverty – By providing an income in retirement, pension schemes ensure that the scheme members do not experience old age poverty where they have to rely on their family, relatives and friends for survival
- Home Ownership - Savings in a pension scheme can help you achieve your dream of owning a home. This can be done through a mortgage or a direct residential house purchase using your pension savings. A member may assign up to 60% of their pension benefits or the market value of the property, whichever is less, to provide a mortgage guarantee. The guarantee may enable the member to acquire immovable property on which a house has been erected, erect a house, add, or carry out repairs to a house, secure financing or waiver, as the case may be, for deposits, stamp duty, valuation fees and legal fees and any other transaction costs required. On the other hand, a pension scheme member may utilize up to 40% of their benefits to purchase a residential house directly subject to a maximum allowable amount of Kshs 7 Mn and the amount they use should not exceed the buying price of the house.
Section 2: Types of Retirement Benefits Schemes
A retirement benefits scheme, is a savings avenue that allows contributing individuals to make regular contributions during their productive years into the scheme and thereafter get income from the scheme upon retirement.
The retirement benefits system in Kenya has three pillars as follows:
- Zero Pillar – This pillar refers to the state-funded pension for citizens over the age of 65 and provides a basic income. This is managed by the Ministry in charge of social protection. Currently in Kenya through the Older Persons Cash Transfer program, the amount paid is Kshs 2,000 per household per month delivered every two months through appointed payment agent to poor and vulnerable persons over the age of 65 years. As the end of the financial year 2015/2016, the program covered 203,111 households,
- First Pillar – The first pillar is mandatory to all workers. The mandatory contribution is by both employer and employees and it targets workers in both the formal and informal sectors. This is where the National Social Security Fund (NSSF) comes in, and
- Second Pillar – This pillar is categorized by the voluntary nature of all schemes that fall under it. It includes both individual and employer-based pension schemes and is what we hall focus on in the analysis of the different pension schemes in the market below.
Other than the NSSF, the rest of the pension schemes in the country fall under the second pillar. It is important that before joining any pension scheme you learn how they operate so that you make a more informed decision. The schemes here can be categorized in four different ways depending on contributions, mode of payment at retirement, type of membership and mode of investment.
I. Based on contributions
Under this category, there are two types of pension schemes, namely, Defined Contributions Schemes and Defined Benefits Schemes. These can be differentiated as below:
|
Defined Contribution (DC) Scheme |
Defined Benefits (DB) Scheme |
|
|
CONTRIBUTIONS |
§ Member’ and employer’ contributions are fixed/defined either as a percentage of pensionable earnings or as a shilling amount § However, members have the freedom to contribute more than the defined rate (Additional Voluntary Contribution) |
§ Defined benefit plans are funded either exclusively by employer contributions or sometimes require employee contributions § An actuary estimates the cost of the promises being earned each year, to advice on the required amount that needs to be contributed each year to keep the scheme healthy. |
|
BENEFITS |
§ Member’s retirement benefits have a value equal to those contributions, net of expenses (e.g. insurance premiums) accumulated in an individual account with investment return and any surpluses or deficits as determined by the trustees of the scheme |
§ The benefits, which is ordinarily determined by the scheme rules, are defined in advance through a formula detailed in the Trust Deed § Benefits are often related to the final salary and/or years of service of the employee § The employer is then responsible for making sure that there are enough funds to enable them to fulfil this promise |
|
§ Uncertainty of benefits - difficult for a member to know in advance how much pension they will be able to secure at retirement |
§ The certainty of benefits (easy to measure benefits in terms of adequacy and better for retirement planning) |
|
|
RISK |
§ Risk of investment performance |
§ Risk of solvency of employer |
Changes in demographics, volatile interest rates, lower expected returns and the greater mobility in today’s workforce which has in some way made DC schemes more attractive to employers and employees.
II. Mode of payment at retirement
Ultimately, the aim of a retirement benefits scheme is to provide an income in retirement; however, upon retiring, not all schemes are the same. On one hand, we have pension schemes that are schemes where at retirement, a member of a pension scheme may access up to a third of their contributions and contributions made on their behalf plus accrued interest as a lump sum. The remainder is used to purchase an annuity (pension) that pays a periodic income to the pensioner in their retirement years, usually, monthly.
On the other hand, there are provident funds. At retirement, a member of a provident fund receives their contribution and contributions made on their behalf plus accrued interest as a lump sum.
It is key to also note the existence of Income drawdown funds which provide individuals and members of retirement benefits schemes with an option to access their benefits as a regular income through an investment fund upon retirement rather than taking up an annuity or a lump sum. In an income drawdown a retiree or any scheme member over the age of 50 years, may transfer their benefits from their current scheme to the income drawdown fund. The benefits are locked in the fund for a minimum period of 10 years while giving the member the ability to withdraw up to a maximum of 15% per annum of their fund balance every year. The remaining balance in the fund is invested and grows in the period of the 10 years.
III. Type of membership
Under this categorization, we have three main types of pension schemes as follows:
Occupational Retirement Benefits Schemes – These are schemes that are set up by an employer where only members of staff of the organization are eligible to join
Umbrella Retirement Benefits Schemes - These are schemes that pool the retirement contributions of multiple employers on behalf of their employees thereby reducing the average cost per member and enhancing the overall returns of both the employer and the employees’ contributions
Individual/Personal Retirement Benefits Schemes - These are schemes where individuals contribute directly into the scheme towards saving for their retirement. The contributions may be flexible to accommodate an individual’s financial circumstances.
IV. Mode of investment and governance
Under categorization by mode of investment, pension schemes may be said to either segregated or guaranteed. Below we explain the difference between the two:
Segregated Funds: In these schemes, members’ contributions are invested directly by the Trustees via an appointed Fund Manager. The Trustees establish an appropriate Investment Policy which is then implemented by the Fund Manager. The scheme directly holds the investments and the returns are fully accrued to the scheme for the benefit of members
Guaranteed Funds: This is a scheme offered by insurance companies where the members’ contributions are pooled together. The insurance company guarantees a minimum rate of return that should not exceed 4% p.a. by law and should the actual return surpass the minimum guaranteed rate, the insurance company tops up the minimum rate with a bonus rate of return
Section 3: Pension Historical Performance (Segregated vs Guaranteed) and Asset Allocation
Historical Asset Allocation
Every Retirement Benefits Scheme must formulate an Investments Policy Statement (IPS) which guides how investments are to be done. The IPS outlines the process for a retirement benefits schemes’ investment-related decision making as well as the investment limits per each asset class and even the securities that the fund can invest in. The IPS should however not conflict with the limits dictated by the RBA Investment Guidelines (Table G). The table contains the maximum allowable limits for investments in the named asset classes and these limits are contained in the last column in the table below. The IPS of the various schemes vary as the characteristics of members differ. For example, a pension scheme with relatively many members nearing the retirement age will not invest too much in long-term and illiquid asset classes such as Immovable Property, and the scheme’s IPS will reflect this.
The chart below indicates how the industry assets have been invested over time:
|
Kenyan Pension Funds Asset Allocation |
|||||||||
|
|
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
Average |
Allowable Limit |
|
Government Securities |
33.8% |
31.0% |
29.8% |
38.3% |
36.5% |
39.4% |
42.5% |
35.9% |
90.0% |
|
Quoted Equities |
25.5% |
26.0% |
23.0% |
17.4% |
19.5% |
17.3% |
17.7% |
20.9% |
70.0% |
|
Immovable Property |
17.2% |
17.0% |
18.5% |
19.5% |
21.0% |
19.7% |
18.0% |
18.7% |
30.0% |
|
Guaranteed Funds |
10.3% |
11.0% |
12.2% |
14.2% |
13.2% |
14.4% |
15.2% |
12.9% |
100.0% |
|
Listed Corporate Bonds |
4.4% |
6.0% |
5.9% |
5.1% |
3.9% |
3.5% |
1.5% |
4.3% |
20.0% |
|
Fixed Deposits |
4.9% |
5.0% |
6.8% |
2.7% |
3.0% |
3.1% |
3.0% |
4.1% |
30.0% |
|
Offshore |
2.2% |
2.0% |
0.9% |
0.8% |
1.2% |
1.1% |
0.5% |
1.2% |
15.0% |
|
Cash |
1.3% |
1.0% |
1.4% |
1.4% |
1.2% |
1.1% |
1.1% |
1.2% |
5.0% |
|
Unquoted Equities |
0.6% |
1.0% |
0.4% |
0.4% |
0.4% |
0.3% |
0.4% |
0.5% |
5.0% |
|
Private Equity |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.1% |
0.1% |
0.0% |
10.0% |
|
REITs |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.1% |
0.1% |
0.1% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
30.0% |
|
Commercial Paper, non-listed bonds by private companies* |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
10.0% |
|
Others e.g. Unlisted Commercial Papers |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
10.0% |
|
Total Assets |
100% |
100% |
100% |
100% |
100% |
100% |
100% |
|
|
It is good to note that the bulk of the investments are in Government securities, Equities and immovable properties in that order. The schemes are yet to take advantage of the new asset classes like Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and Derivatives.
Historical Performances
Some of the different factors that determine the performance of pension schemes include:
- Asset allocation: This is the proportion of the assets that are invested in a certain asset class
- Security Selection: This is the ability to select the best performing security within a specific asset class
- Size of the Scheme
- Investment Horizon
- Risk appetite
In the graph below, we look at the performance of retirement Schemes over the last seven years, focusing on the performances of guaranteed and segregated funds:
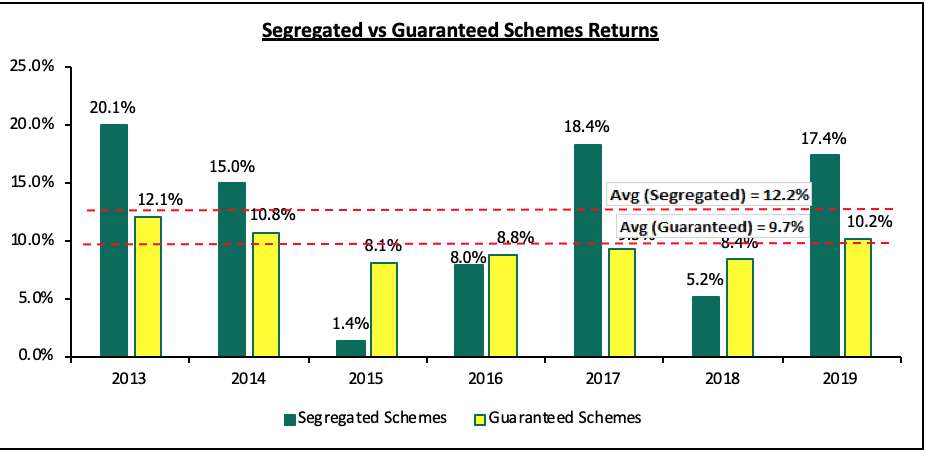 Sources: a. Segregated Schemes Performances – ACTSERV and Zamara Z-CASS Surveys
Sources: a. Segregated Schemes Performances – ACTSERV and Zamara Z-CASS Surveys
b. Guaranteed Schemes – Cytonn Research with data collected from 18 Approved Issuers since 2001
From the above chart, it is evident that segregated funds have outperformed guaranteed funds – with the average performance of the Guaranteed Funds over the last 7 years has been 9.7% p.a. whereas Segregated Schemes have enjoyed a higher return of 12.2% p.a.
It is important to note that on average members and pension trustees should aim to gain returns that are above inflation at all times. Also, the aim for fund managers to perform better than the various benchmarks set out in the Investment Policy Statements.
Section 4: Impact of Covid-19 on Retirement Benefits Schemes
The currently ongoing pandemic, Covid-19, has had a significant impact on capital and financial markets performances. Pension schemes have also been affected as they invest their members’ savings in the same economic environment. Some of the key impacts that the pandemic has had on retirement schemes include:
- A decrease in the value of assets in retirement savings accounts from falling financial markets;
- An increase in liabilities for guaranteed and defined benefits schemes;
- A lower capability to contribute to retirement savings plans by individuals, and by both employers and employees;
- Operational disruptions as a result of working remotely;
- Low to negative returns which impacts the overall retirement income adequacy
The best advice to members is, however, to stick to your pension savings plan and keep contributing, as long as they are in a position to. If one does not have a pension plan then they will be better off starting one and making contributions as well.
Some pension scheme members may want to withdraw their pension because they are afraid their money is losing value. However, by doing this, the member helps in crystallizing the decline in value. To prevent this they should delay taking their pension if they can. It is key for members to have a long term view and to allow the income planning and generation course to runs its course as dips in the market are a common occurrence and the market will eventually recover.
Section 5: Access to Your Pension Savings
Withdrawing from a pension scheme is highly discouraged as it foils the retirement plan one has and may end up reducing their income replacement ratio at retirement. It is good to note that the target is that one should have an income replacement ratio of about 75% if they are to lead the same quality of life they had before retirement. However, it remains an allowable provision, should the need arise and the members have no alternative source of fund. There are two ways one can access their pension benefits:
- Early Leaving
For a member that opt to leave a scheme early before attaining the retirement age, they have the following options:
- Transfer - to transfer their savings to another registered retirement benefits scheme.
- Deferral – to leave their savings in the scheme as a Deferred Member’s Account which the member may access on or after the age of fifty.
- Withdrawal - A member may withdraw from the scheme in lump sum an amount not exceeding their portion of savings plus 50% of the employer’s portion. The remaining 50% will be retained in the scheme until the member retires, opts to transfer the benefits to another registered retirement benefits scheme or emigrates to another country with no present intentions of returning to reside in Kenya.
- Emigration - a member who has emigrated from Kenya and has no intentions of returning to reside in Kenya can access all of their savings including the whole of the employer portion.
2. Retirement
The second way of accessing one’s pension savings is after you retire. The benefits may be accessed either as a lump sum, as a pension or transferred to an income drawdown fund as explained in Section 2.
Section 5: Conclusion - Factors To Consider Before Joining a Pension Scheme
Financial Planning for Retirement is a vital need for everyone and the earlier one starts the better. Starting early also means that you will be to take full advantage of the compounded growth of your savings and have a larger retirement pot when you retire.
There are several key factors that one should consider before joining a retirement benefits scheme or when re-evaluating their current scheme choice, these include:
- Returns – The return rate of your pension provider should be high enough to ensure a sizeable growth for pension savings and a member may choose where they get the highest return so that they ensure a higher income replacement ratio is attained. The rate should especially be higher than the inflation rate – this way your money is not losing value over time,
- Affordability and Flexibility – Choosing a retirement plan that you can make contributions without too much strain is key. You are likely to stick to a plan which you easily make contributions to. At the same time, the flexibility the plan offers in terms of changing the contribution amount and measures, if any, should you miss a contribution are key considerations,
- Understand the different options at hand – It is vital that before you join a scheme you understand how your money will be treated, the access options and how they will be paid out to you at retirement to ensure that your pension scheme features to match your goals. Different schemes may also have different provisions on the utilization of your savings to secure a mortgage facility or purchase a residential house, and,
- Choose a manager you trust – As mentioned previously, retirement planning is a long term affair and it is best that you have a pension provider that you can trust. Good governance structures and management experience are two of many aspects you can use to evaluate your pension plan provider.
- Additional Benefits: It is good to find out what are the other benefits that come with a retirement fund such as insurance covers and ensure you take advantage of the same.
People’s behavior toward retirement planning is intrinsically influenced by one’s attitude, knowledge, and information. By understanding the inevitability of retirement, the importance of retirement planning and what power of choice you have as an investor then you can be able to make a sound decision that ensures you enjoy the sunset years of your life.
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this publication are those of the writers where particulars are not warranted. This publication is meant for general information only and is not a warranty, representation, advice or solicitation of any nature. Readers are advised in all circumstances to seek the advice of a registered investment advisor.

