Jul 5, 2020
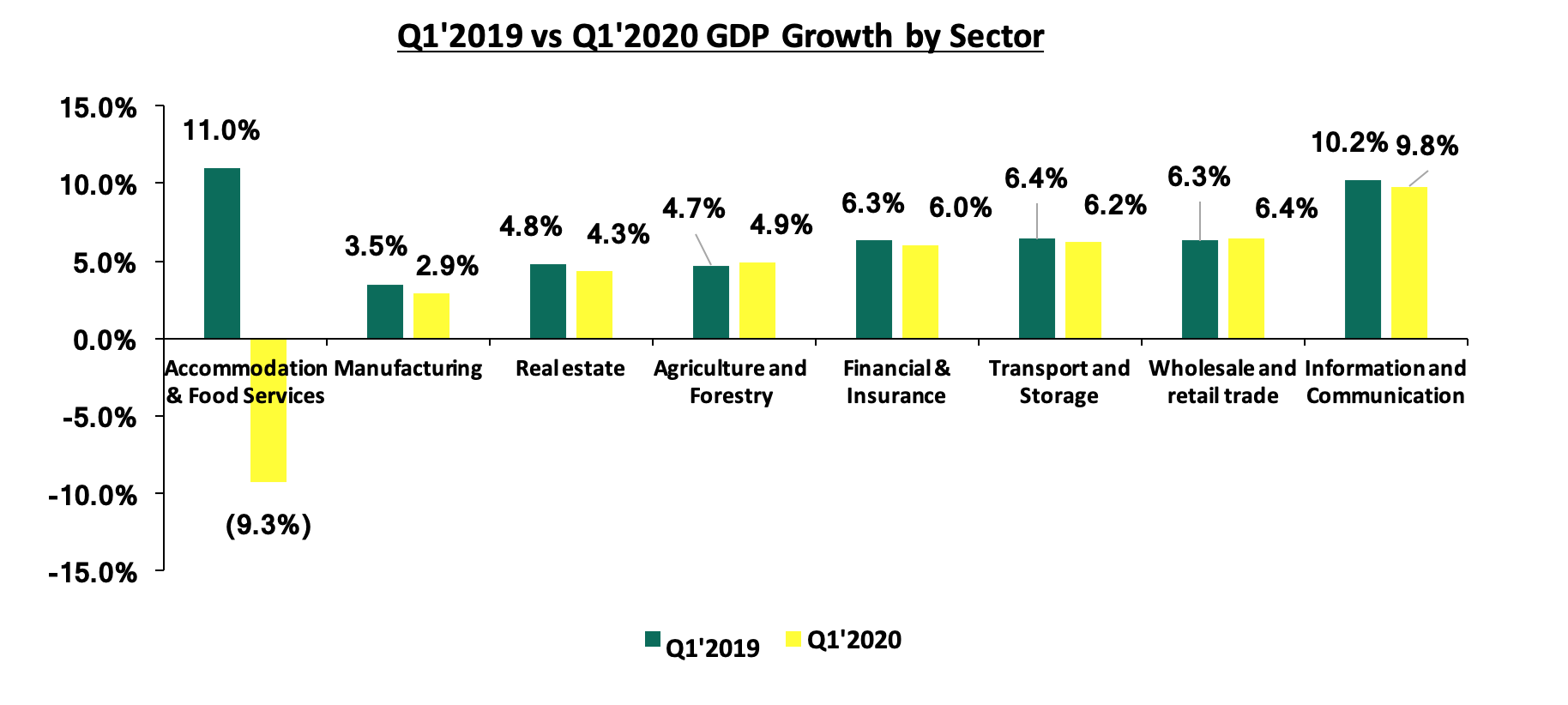
Economic growth for Kenya is projected to be significantly lower with the IMF projecting a growth of 1.0% while the treasury projected 2.5% growth. For the first quarter of 2020, the impact of the virus had not taken a big toll and we saw growth coming in at 4.9%, a 2 – year low, compared to 5.5% recorded in a similar period of review in 2019.
The chart below shows the Q1’2019 and Q1’2020 GDP growth by sector;
Below are the sectorial Q1’2020 GDP contributions;
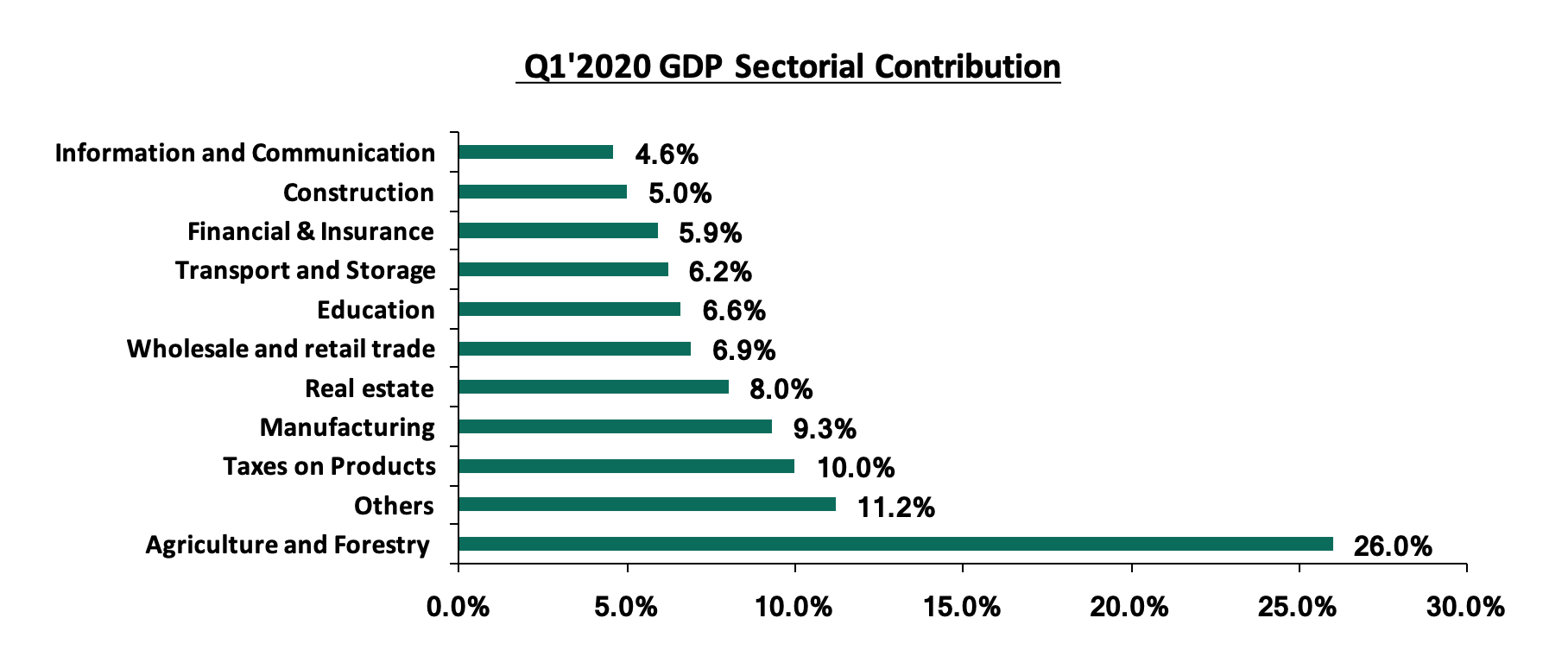
For more information, see our Q1’2020 GDP Note;
According to Stanbic Bank’s Monthly Purchasing Manager’s Index (PMI), released earlier during the week, the seasonally adjusted PMI came in at 46.6 in June, an improvement from 36.7 in May 2020 and higher than the H1’2020 average of 42.2 but lower than the H1’2019 average of 51.7. The lower PMI is due to lower business revenues in sectors like the Tourism and Hospitality sectors that have witnessed significant layoffs. A PMI reading of above 50 indicates improvements in the business environment, while a reading below 50 indicates a worsening outlook. The slow decline in output and new orders was due to the reduction in curfew hours as well as relaxed measures in Europe thus improving demand for exports. This saw employment numbers fall at the slowest pace in the last three months. Input costs declined for the third month in a row due to lower wage costs.
The International Monetary Fund released the first chapter of the World Economic Outlook (The Great Lockdown), where they revised Kenya’s 2020 GDP growth rate for 2020 to 1.0%, from the 6.0% growth rate projected at the beginning of the year. For more information, see our, Cytonn Weekly #16/2020.
Inflation:
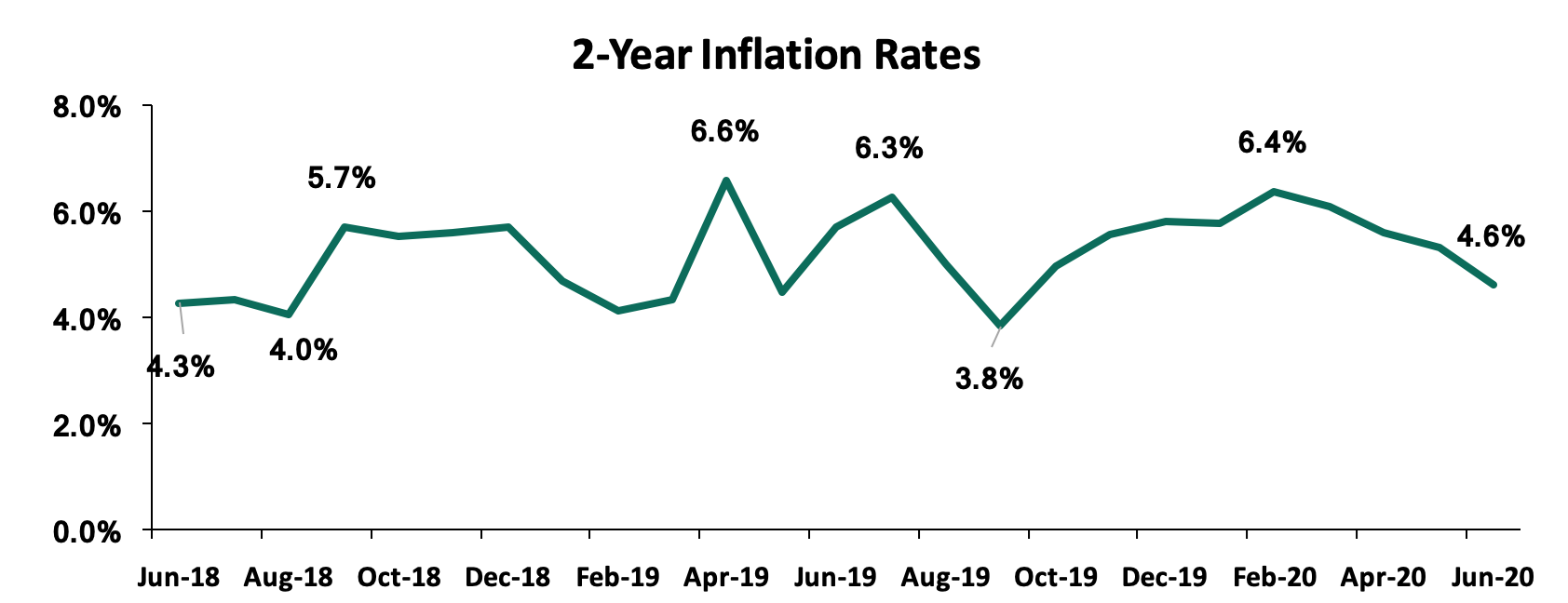
Inflation rates have remained relatively stable and we saw the average inflation rate rising to 5.6% compared to 5.0% recorded in H1’2019. In a bid to ensure that the inflation basket is representative of what is happening on the ground, KNBS, revised the components of the Inflation basket some of the items increased include; mobile phone airtime, pay-tv, and garbage collection while they dropped archaic items such as radio and video cassettes. The revision brings the number of items included in the commodity basket to 330 from 234 while data collection zones have increased from the previous 25 to 50. KNBS also adjusted the weighting assigned to items in the commodity basket such as the Food and Non-Alcoholic Beverages, Alcoholic Beverages, Tobacco and Narcotics, and Transport Indices, which previously had a weighting of 36.0%, 2.1%, and 8.7%, respectively, to 32.9%, 3.3%, and 9.7%, respectively.
For the month of June, inflation came in at 4.7% with the m/m inflation decreasing marginally by 0.3%. The decrease in the month-on-month inflation in June was mainly due to:
- A 1.3% decrease in the food and non-alcoholic beverage index, driven by a decrease in prices of some food items such as tomatoes, Irish potatoes, and cabbages, which decreased by 12.2%, 5.1%, and 4.8%, respectively,
- A 0.8% decrease in Housing, Water, Electricity, Gas and Other Fuels Index stimulated by a 21.3% decrease in prices of kerosene which offset the 0.9% increase in electricity, and,
- The decrease was however weighed down by the 2.1% increase in transport cost driven by a 6.8% increase in pump prices for petrol which outweighed the 4.8% decrease in the cost of diesel.
We expect inflation to remain stable despite supply-side disruption due to COVID-19 as low demand for commodities compensates for the cost-push inflation, coupled with the low oil prices in the international markets. The recent reopening of a majority of the global markets will also address supply chain issues causing import prices to stabilize.
Below is the trend analysis of the inflation figures for the last two years:
The Kenya Shilling:
The Kenya Shilling depreciated by 5.1% against the US Dollar in H1’2020, to close at Kshs 106.5, from Kshs 101.3 at the end of December 2019, attributable to high dollar demand from foreigners exiting the market as they direct their funds to safer havens. At the tail end of the period review, there was increased dollar demand from merchandise importers as the easing of coronavirus restrictions jumpstarted economic activities thus boosting demand for hard currency.
Some of the key challenges facing the currency include:
- A deteriorating current account position: we saw current account deficit deteriorated by 10.2% during Q1’2020, coming in at Kshs 110.9 bn, from Kshs 100.6 bn in Q1’2019 attributable to;
- 3.0% decline in the secondary income (transfers recorded in the balance of payments whenever an economy provides or receives goods, services, income or financial items) balance, to Kshs 124.1 bn, from Kshs 128.0 bn in Q1’2019, and,
- A 67.0% decline in the services trade balance (the difference between the imports and exports of services) to Kshs 20.4 bn, from Kshs 61.9 bn. For more information see our Q1’2020 BOP Note
- Demand from merchandise and energy sector importers as they beef up their hard currency positions amid a slowdown in foreign dollar currency inflows, and,
- Subdued diaspora remittances evidenced by the 9.0% decline to USD 208.2 mn in April 2020, from USD 228.8 seen the previous month, mainly due to the decline in economic activities globally, coupled with increased prices of household items leading to lower disposable income. Key to note, the Central Bank of Kenya (CBK) expects a 12.0% decline in remittances in 2020.
The shilling is however expected to be supported by:
- High levels of forex reserves, currently at USD 9.7 bn (equivalent to 5.8-months of import cover), above the statutory requirement of maintaining at least 4.0-months of import cover, and the EAC region’s convergence criteria of 4.5-months of import cover.
Monetary Policy:
After holding the Central Bank rates Stable last year the monetary policy Committee in a bid to support the economy met five times reducing the Central Bank Rate CBR) to 7.00% from 8.25% at the beginning of the year. In addition to the CBR rate, the Cash Reserve Ratio was also reduced to 4.25%, from 5.25% to provide liquidity to banks for onward lending.
H1’2020 Key Highlights:
During the period of review, the government was able to receive funds from international organizations to help the country fight against the negative effects of the pandemic. For more information, see our Cytonn Weekly #19/2020 and Cytonn Weekly #20/2020. The table below shows the funds the government has received so far towards supporting the economy during the Coronavirus pandemic period;
|
Entity |
Amount Received in Kshs bn |
|
Central Bank of Kenya |
7.4 |
|
International Monetary Fund |
78.7 |
|
International Development Association (IDA) |
80.0 |
|
World Bank |
80.0 |
|
International Bank for Reconstruction and Development |
26.6 |
|
Total |
272.7 |
- Finance Act 2020
During H1’2020, the president signed into law, the Finance Bill 2020. Below are some of the key highlights affecting investments decisions more directly:
- Under the Income Tax Act, the key highlights included:
- Extending the upper limit of the Residential Income Tax to Kshs 15.0 mn from Kshs 10.0 mn to allow landlords with rental income of between Kshs 288 and Kshs 15.0 mn to access the more concessional tax rate of 10% of gross income, and reduce administrative costs of ascertaining profit for such landlords,
- Introduction of a minimum tax, to be introduced at a rate of 1.0% of the gross turnover. This new tax will apply to all persons whether they’re making profits or incurring losses.
- Introduction of Digital Service Tax, to be introduced at a rate of 1.5% of the gross transaction value, to be charged on individuals who generate income from the provision of services through the digital market place., and,
- Some allowable items such as (i) any entrance fee or annual subscription paid during that year of income to a trade association, (ii) capital expenditure on expenses relating to authorization and issue of shares, debentures or similar securities offered for purchase, listing on any securities exchange and acquiring a rating for purposes of listing, (iii) income from a registered home ownership savings plan, and, (iv) Income from employment paid in the form of bonuses, overtime, and retirement benefits to employees whose taxable employment income before bonus and overtime allowances does not exceed the lowest tax band will now not be tax allowable.
- Introduction of taxation of lump sum payments from Retirement Benefits schemes for people
2020/2021 Budget
During H1’2020 the Cabinet Secretary for the National Treasury read the FY’2020/21 budget. Some of the highlights from the budget included;
- The total FY’2020/21 budget is estimated at Kshs 3.2 tn, a 2.6% increase from the Kshs 3.1 tn revised FY’2019/20 budget, mainly due to an 18.1% increase in the Consolidated Fund Services (CFS) to Kshs 1.0 bn from Kshs 0.9 bn in the FY’2019/20 revised estimates. The increase in Consolidated Fund Services expenditures is mainly as a result of an increase in public debt servicing expenses which will form 88.0% of the total CFS expenditure,
- For the financial year 2020/2021, the government projects that total revenue will contract by 2.1% to Kshs 1.85 tn from the Kshs 1.89 tn in FY’2019/2020. The decline is mainly due to a 1.3% decline in ordinary revenue to Kshs 1.62 tn from an estimated Kshs 1.64 tn,
- Total expenditure is set to decline by 2.2% to Kshs 2.71 tn from Kshs 2.74 tn as per the revised FY’2019/20 Budget. The Treasury estimates that the post-COVID-19 Economic Stimulus Package will cost Kshs 53.74 bn, and,
- Public debt is expected to continue growing in FY’2020/21 as the approximate Kshs 822.7 bn fiscal deficits will be financed through both domestic and foreign debts. The fiscal deficit (excluding grants) as a share of GDP, is expected to come in at 7.6% in FY’2020/2021 from 5.6% in FY 2019/2020. For more information, see our FY 2020/2021 Pre-Budget Discussion Note
Of the 7 indicators, we track, security and inflation are positive, investor sentiments is neutral and government borrowing, exchange rate, interest rates, and GDP are negative. We have switched our outlook on the 2020 macroeconomic environment from positive to negative depending on how fast the Coronavirus is contained.

