Jun 14, 2020
Following the release of the Q1’2020 results by Kenyan listed banks, the Cytonn Financial Services Research Team undertook an analysis on the financial performance of the listed banks and identified the key factors that shaped the performance of the sector, and our expectations of the banking sector for the rest of the year.
Asset quality deteriorated in Q1’2020 with the gross NPL ratio increasing by 0.9% points to 11.3% from 10.4% in Q1’2019. This was high compared to the 5-year average of 8.5%. In accordance with IFRS 9, banks are expected to provide both for the incurred and expected credit losses. Consequently, this saw the NPL coverage increase to 57.4% in Q1’2020 from 54.5% in Q1’2019 as banks adopted a cautious stance on the back of the expected impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The report is themed “Deteriorating Asset Quality amid the COVID-19 Operating Environment” as we assess the key factors that influenced the performance of the banking sector in Q1’2020, the key trends, the challenges banks faced, and areas that will be crucial for growth and stability of the banking sector going forward. As such, we shall address the following:
- Key Themes That Shaped the Banking Sector Performance in Q1’2020,
- Summary of The Performance of the Listed Banking Sector in Q1’2020,
- The Focus Areas of the Banking Sector Players Going Forward, and,
- Brief Summary and Ranking of the Listed Banks based on the Outcome of Our Analysis.
Section I: Key Themes That Shaped the Banking Sector Performance in Q1’2020
Below, we highlight the key themes that shaped the banking sector in Q1’20120 which include regulation, consolidation, asset quality, and capital conservation:
- Regulation - The impactful regulations of the banking sector included the Guidance on loan restructuring:
a) Guidance on Loan Restructuring: The Central Bank of Kenya on March 27th, 2020 provided commercial banks and mortgage finance companies with guidelines on loan reclassification, and provisioning of extended and restructured loans as per the Banking Circular No 3 of 2020. The key takeouts from the circular included:
-
- Central Bank stipulated that banks would be allowed to extend loan repayments for their customers for a period not more than one year,
- The cost of restructuring and extension of loans would be met by the banks and the banks would have to report any restructuring in relation to the COVID-19 pandemic to the Central Bank monthly,
- Banks would be required to keep a record of all restructured and extended loans with the details of how the pandemic has affected specific customers whose loans are restructured and monitoring measures adopted by the bank, and,
- Personal loans that have been extended or restructured by banks would not be subjected to the classification of renegotiated loans stipulated in CBK’s prudential guidelines meaning that banks would not have to classify the loans as non-performing loans.
Following this guideline, most commercial banks have moved to restructure loan repayments for their customers. The table below shows some of the major banks that have moved to restructure loans for their customers;
|
No. |
Bank |
Amount Restructured (Kshs bn) |
% of restructured loans to total loans |
y/y Change in Loan loss provision |
|
1 |
Kenya Commercial Bank |
120.2 |
21.7% |
149.1% |
|
2 |
Absa Bank Kenya |
8.3 |
4.1% |
75.2% |
|
3 |
Standard Chartered Bank of Kenya |
22.0 |
17.5% |
3.1% |
|
4 |
Diamond Trust Bank |
40.7 |
18.3% |
52.0% |
|
5 |
Co-operative Bank of Kenya |
15.3 |
5.5% |
79.5% |
|
6 |
Equity Group Holdings |
92.0 |
24.3% |
660.4% |
|
|
Total |
298.5 |
|
|
2. Consolidation: Consolidation activity remained one of the highlights witnessed in Q1’2020, in line with our expectations, as players in the sector were either acquired or merged, leading to the formation of relatively larger, well-capitalized, and possibly more stable entities. The following were the major M&A’s activities witnessed during the quarter:
- On 27th January 2020, Nigerian lender, Access Bank PLC completed the acquisition of a 100% stake in Transnational Bank PLC for an undisclosed amount, with Access Bank PLC targeting to enhance its corporate and retail banking business in Kenya through the acquisition. Access Bank is Nigeria’s largest lender by assets, with an asset base of USD 16.7 bn (equivalent to Kshs 1.7 tn) as at Q1’2020. The deal will see Nigerian banks deepen their presence in Kenya with the United Bank of Africa (UBA) and Guarantee Trust Bank already in the market. For more information on the transaction, see Cytonn Weekly #03/2020,
- On 7th April 2020, the Central Bank of Kenya (CBK) approved the acquisition of a 51.0% stake in Mayfair Bank Limited by an Egyptian lender, Commercial International Bank (CIB), effective 1st May 2020 for an undisclosed amount. The Central Bank of Kenya (CBK) welcomed the transaction, citing it will diversify and strengthen the resilience of the Kenyan banking sector. Commercial International Bank, Egypt’s leading private sector bank, has an asset base of USD 24.2 bn (Kshs 2.5 tn) as of December 2019. CIB’s business model focusses on individuals, SMEs, institutions, and corporates and will be the first Egyptian bank to establish a presence in Kenya. The deal will see CIB provide Mayfair Bank Limited with the requisite skills, resources, and infrastructure to scale up its business. For more information on the transaction, see Cytonn Weekly #17/2020,
- On 4th May 2020, the Central Bank of Kenya approved the acquisition of Imperial Bank’s assets and assumption of liabilities worth Kshs 3.2 bn each by KCB Group effective 2nd June 2020. The move will see Imperial Bank depositors paid a total of Kshs 3.2 bn over a period of 4 years and will have cumulatively recovered 37.3% of the deposits since 2015 when payments commenced, with a bulk of the deposits amounting to Kshs 53.3 bn remaining with Kenya Deposit Insurance Corporation (KDIC). Imperial Bank was put under receivership (a process that can assist creditors to recover funds in default and can help troubled companies to avoid bankruptcy) in October 2015 due to inappropriate banking practices, with the CBK transferring Imperial Bank’s management and control to the KDIC. For more information on the transaction, see Cytonn Weekly #21/2020,
Other mergers and acquisitions activities announced recently include;
- Equity Group Holdings, in its expansion strategy, has various on-going acquisitions in the region having entered into a binding term sheet with Atlas Mara Limited to acquire certain banking assets in 4 countries in exchange for shares in Equity Group which are inclusive of:
- 62.0% of of the share capital of Banque Populaire du Rwanda (BPR);
- 100.0% of the share capital of Africa Banking Corporation Zambia (ABCZam) Ltd;
- 100.0% of the share capital of Africa Banking Corporation Tanzania (ABCTz), and;
- 100.0% of the share capital of Africa Banking Corporation Mozambique Ltd (ABCMoz).
These acquisitions will allow Equity Group Holdings an easy penetration into these four African countries. Successful completion of the above transactions will likely see Equity expand its regional footprint, aiding the bank’s performance. Read more information on the same here,
- Co-operative Bank of Kenya announced it has opened talks to acquire a 100.0% stake of Jamii Bora Bank Limited. The announcement came months after Commercial Bank of Africa (CBA), dropped its cash buy-out offer and instead, merged with NIC Bank to form NCBA Group. Read more information on the same here, and,
- Equity group was also given the green light by the Committee Responsible for Initial Determination (CID), a Commission mandated to monitor and investigate possible breaches of the COMESA Competition Regulations, to acquire a 66.5% controlling stake worth Kshs 10.9 bn in Banque Commerciale du Congo (BCDC), effectively valuing BCDC at Kshs 16.4 bn. The transaction will see Equity Group pay Kshs 17,430 per share to acquire 625,354 shares in BCDC, a deal inclusive of dividends issued as at 1st January 2020, from the George Arthur Forrest family, and will see Equity integrate the bank with its subsidiary, Equity Bank Congo, to create the second-largest bank in Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Read more on the same here
Below is a summary of the deals in the last 5-years that have either happened, been announced or expected to be concluded:
|
Acquirer |
Bank Acquired |
Book Value at Acquisition (Kshs. Bns) |
Transaction Stake |
Transaction Value |
P/Bv Multiple |
Date |
|
Commercial International Bank |
Mayfair Bank Limited |
1.0 |
51.0% |
Undisclosed |
N/A |
May-20* |
|
Co-operative Bank |
Jamii Bora Bank |
3.4 |
100.0% |
Undisclosed |
N/A |
Mar-20* |
|
Access Bank PLC (Nigeria) |
Transnational Bank PLC |
1.9 |
100.0% |
Undisclosed |
N/A |
Jan-20** |
|
Oiko Credit |
Credit Bank |
3.0 |
22.8% |
1.0 |
1.5x |
Aug-19 |
|
KCB Group |
National Bank of Kenya |
7.0 |
100.0% |
6.6 |
0.9x |
Sep-19 |
|
CBA Group |
NIC Group |
33.5 |
53%:47% |
23.0 |
0.7x |
Sep-19 |
|
CBA Group** |
Jamii Bora Bank |
3.4 |
100.0% |
1.4 |
0.4x |
Jan-19 |
|
AfricInvest Azure |
Prime Bank |
21.2 |
24.2% |
5.1 |
1.0x |
Jan-19 |
|
KCB Group |
Imperial Bank |
3.2 |
Undisclosed |
Undisclosed |
N/A |
Dec-18 |
|
SBM Bank Kenya |
Chase Bank Ltd |
Unknown |
75.0% |
Undisclosed |
N/A |
Aug-18 |
|
DTBK |
Habib Bank Kenya |
2.4 |
100.0% |
1.8 |
0.8x |
Mar-17 |
|
SBM Holdings |
Fidelity Commercial Bank |
1.8 |
100.0% |
2.8 |
1.6x |
Nov-16 |
|
M Bank |
Oriental Commercial Bank |
1.8 |
51.0% |
1.3 |
1.4x |
Jun-16 |
|
I&M Holdings |
Giro Commercial Bank |
3.0 |
100.0% |
5.0 |
1.7x |
Jun-16 |
|
Mwalimu SACCO |
Equatorial Commercial Bank |
1.2 |
75.0% |
2.6 |
2.3x |
Mar-15 |
|
Centum |
K-Rep Bank |
2.1 |
66.0% |
2.5 |
1.8x |
Jul-14 |
|
GT Bank |
Fina Bank Group |
3.9 |
70.0% |
8.6 |
3.2x |
Nov-13 |
|
Average |
75.7% |
1.4x |
||||
|
*Announcement date ** Deals that were dropped |
||||||
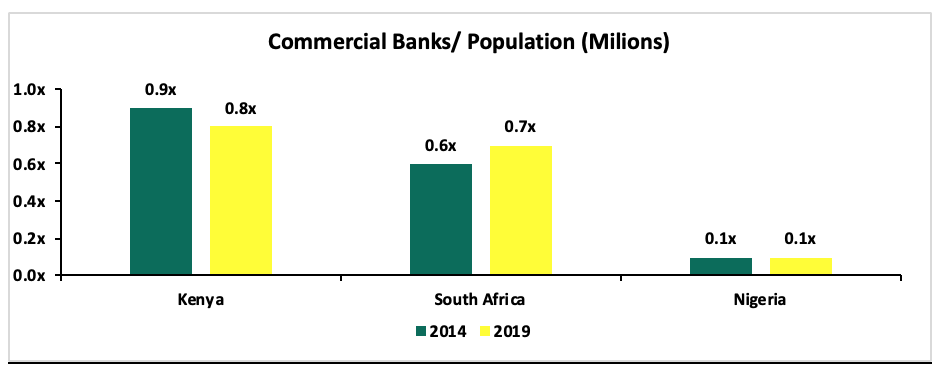
The number of commercial banks in Kenya has now reduced to 38, compared to 43 banks from 5-years ago. The ratio of the number of banks and Kenya’s 47.6 million people now stands at 0.8x, compared with a ratio of 0.9x, 5-years ago. The ratio is improving, however, Kenya still remains overbanked as the number of banks remains relatively high compared to the population. For more on this see our topical
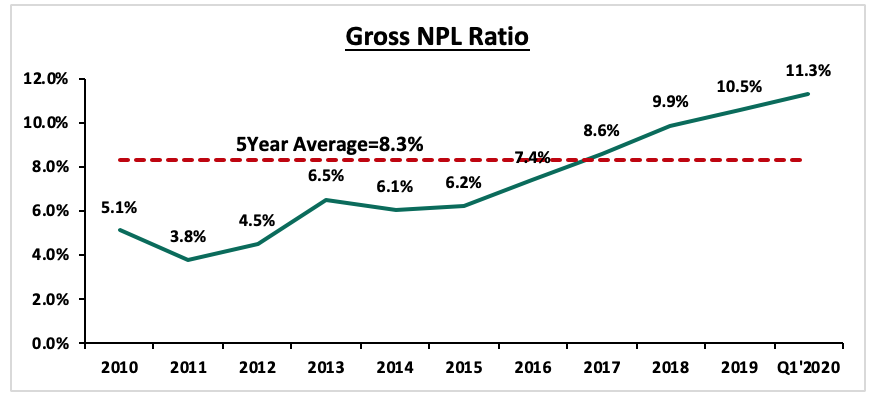
3. Asset Quality - Asset quality deteriorated in Q1’2020 with the gross NPL ratio increasing by 0.9% points to 11.3% from 10.4% in Q1’2019. This was high compared to the 5-year average of 8.5%. In accordance with IFRS 9, banks are expected to provide both for the incurred and expected credit losses. Consequently, this saw the NPL coverage increase to 57.4% in Q1’2020 from 54.5% in Q1’2019 as banks bank adopted a cautious stance on the back of the expected impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. We expect higher provisional requirements to subdue profitability during the year across the banking sector on account of the tough business environment.
In our view, further relaxation of provisioning rules by the Central Bank, as part of the prudential guidelines would be a welcomed move. This would be in the form of adjustment to the loan classification in the different categories, (Normal and watch, Substandard, Doubtful Debts, and Loss, where the loans are now classified as being impaired). The table below highlights the characteristics of the different categories of loans;
|
Loan Classification |
Interpretation |
|
Normal |
· These are well-documented loans granted to financially sound customers. All such loans must be performing per the contractual terms and are expected to continue doing so |
|
Watch |
· Loans in this category may be currently protected and may not be past due but exhibit potential weaknesses which may, if not corrected, weaken the asset or inadequately protect the institution’s position at a future date · Principal or interest is due and unpaid for 30 to 90 days, Interest payments are outstanding for 30 to 90 days or have been refinanced, or rolled over |
|
Substandard |
· The primary sources of repayment are not sufficient to service the debt and the institution must look to secondary sources such as collateral, sale of fixed assets, refinancing, or additional capital injections for repayment. · Principal or interest is due and unpaid for more than 90 days to 180 days |
|
Doubtful |
· Loans in this category have all the weaknesses inherent in a substandard loan plus the added characteristic that the loan is not well secured. These weaknesses make collection in full, based on currently existing facts, conditions, and value, highly questionable and improbable. · Principal or interest is due and unpaid for over 180 days. |
|
Loss |
· Loans, which are considered uncollectible or of such little value that their continuance recognition as bankable assets is not warranted shall be classified |
Source: Central Bank of Kenya
Relaxation on the regulations when it comes to classification on how long before a loan is considered non-performing might see a reduction in the provisions’ requirements, consequently supporting Banks’ bottom line, as well as help conserve Bank's capital position. The NPL ratios has been on the rise over the last years partly also due to the adoption of IFRS 9. The chart below highlights the asset quality trend:
4. Capital Conservation: Some listed companies including listed banks announced that they were suspending cash dividends in a bid to conserve capital amid the current tough operating conditions emanating from the effects of the Coronavirus pandemic. A similar trend has been mirrored globally by both financial and non-financial businesses frantically seeking ways to save money with several regulators around the world encouraging companies to cease the discretionary payments of dividends to shareholders amid the COVID-19 pandemic in order to boost capital. For instance, in the United Kingdom (UK), the seven largest banks sought to cancel dividend pay-outs despite having solid capital bases, due to fears of an economic recession. Some of the banks that have already announced the deferral of dividends payments in Kenya include;
- Equity Group whose Board of Directors withdrew their recommendation to pay a first and final dividend of Kshs 2.5 per share for FY’2019, and instead recommended to shareholders that no dividend being paid. This decision was made after considering the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and the need to conserve cash to enable the company to respond appropriately to the unfolding crisis in terms of supporting its customers through the crisis and directing cash resources to potential opportunities that may arise as economies in which the group operates begin to recover,
- NCBA Group announced it would withhold the final dividend payment of Kshs 1.5 per share, to shareholders totalling to Kshs 2.2 bn for FY’2019. The dividend was to be paid to shareholders registered on the company’s register at the close of business (book closure) on 23rd April 2020. NCBA’s board instead recommended the payment of a stock dividend (bonus Issue) and not a cash dividend, which will be issued to shareholders registered on the company’s register at the close of business on 12 May 2020. The bonus share issue will see shareholders receive one share for every ten held, creating 149.8 mn additional shares, given that the entity currently has 1.5 bn shares listed on the securities exchange. The additional shares are valued at Kshs 4.3 bn based on NCBA’s share price of Kshs 28.75 as at 24 April 2020. The stock dividend valued at Kshs 4.3 bn is more than what the lender would have paid in cash dividend of Kshs 2.2 bn. For more information on this see Cytonn Weekly # 17/2020,
- Standard Chartered Bank announced the postponement of payment of the proposed final dividend of Kshs 15.0 per share for FY’2019 that was scheduled to be paid on 28th May 2020. The lender indicated that given that their 34th Annual General Meeting (AGM) which was to take place on 28th May 2020, remained postponed, the payment of the final dividend would be delayed because approval of the final dividend payment would be at the AGM,
Section II: Summary of the Performance of the Listed Banking Sector in Q1’2020:
The table below highlights the performance of the banking sector, showing the performance using several metrics, and the key take-outs of the performance.
Key takeaways from the table above include:
|
Bank |
Core EPS Growth |
Interest Income Growth |
Interest Expense Growth |
Net Interest Income Growth |
Net Interest Margin |
Non-Funded Income Growth |
NFI to Total Operating Income |
Growth in Total Fees & Commissions |
Deposit Growth |
Growth in Government Securities |
Loan to Deposit Ratio |
Loan Growth |
Return on Average Equity |
|
I&M |
(29.7%) |
5.7% |
7.1% |
4.6% |
5.7% |
7.4% |
38.8% |
12.9% |
8.8% |
(2.6%) |
76.0% |
8.3% |
17.5% |
|
ABSA |
17.0% |
2.8% |
(1.9%) |
4.5% |
7.4% |
9.1% |
15.8% |
(0.2%) |
6.6% |
7.2% |
85.0% |
12.4% |
17.0% |
|
Equity |
(14.1%) |
14.3% |
26.7% |
10.6% |
8.2% |
15.8% |
41.9% |
12.5% |
16.5% |
14.2% |
75.9% |
24.1% |
20.7% |
|
COOP |
(0.3%) |
4.5% |
(4.4%) |
8.5% |
8.2% |
19.0% |
39.9 % |
28.3% |
6.9% |
11.5% |
81.3% |
9.8% |
18.5% |
|
KCB |
8.4% |
20.4% |
26.6% |
18.5% |
8.1% |
30.5% |
34.4% |
33.6% |
34.1% |
52.0% |
74.8% |
19.3% |
20.0% |
|
SCBK |
(16.6%) |
(4.3%) |
(1.3%) |
(5.1%) |
7.2% |
(6.5%) |
32.1% |
(5.2%) |
4.6% |
(13.7%) |
51.5% |
6.8% |
15.8% |
|
Stanbic |
(33.5%) |
(7.1%) |
0.5% |
(11.0%) |
5.5% |
(29.2%) |
43.2% |
(37.6%) |
6.4% |
(19.9%) |
79.8% |
11.8% |
14.1% |
|
DTBK |
3.7% |
(2.4%) |
(9.0%) |
2.9% |
5.7% |
3.4% |
25.4% |
9.6% |
(0.9%) |
1.9% |
73.8% |
6.7% |
12.6% |
|
NCBA *** |
(26.8%) |
6.8% |
8.3% |
5.5% |
3.3% |
25.9% |
49.7% |
49.7% |
9.9% |
66.2% |
63.0% |
2.2% |
10.7% |
|
HF |
N/A |
(7.8%) |
(20.9%) |
13.7% |
4.5% |
(2.0%) |
30.4% |
(3.7%) |
11.8% |
39.3% |
101.1% |
(8.5%) |
0.5% |
|
Q1’2020 Mkt Weighted Average* |
(7.4%) |
8.2% |
11.4% |
7.4% |
7.2% |
15.9% |
22.7% |
24.5% |
14.3% |
14.9% |
74.1% |
14.1% |
17.2% |
|
Q1’2019 Mkt Weighted Average** |
12.2% |
3.6% |
2.5% |
4.5% |
8.0% |
10.7% |
36.0% |
11.2% |
11.0% |
16.1% |
74.0% |
7.7% |
19.2% |
|
*Market cap-weighted as at 02/06/2020 |
|||||||||||||
|
**Market cap weighted as at 31/05/2019 ***The financial statements of the bank have been prepared on a prospective basis (assuming a continuation of CBA), representing Q1’2020 results of NCBA bank (merged bank) with prior year comparatives (Q1’2019) being those of CBA bank. Hence, the results are not comparable on a like for like basis. As such, we have used proforma-combined financials for the two entities. |
|||||||||||||
- The above ten listed Kenyan banks recorded a 7.4% average decline in core Earnings per Share (EPS) compared to a growth of 12.2% in Q1’2019, the depressed earnings recorded in the listed banking sector is partly attributed to the tough operating environment occasioned by the ongoing Coronavirus pandemic, which saw total operating expenses increase by 25.6%, outpacing the 10.3% increase recorded on total operating income,
- The 10 listed Banks, recorded a deposit growth of 14.3%, faster than the 11.0% growth recorded in Q1’2019. Interest expenses on the other hand rose by 11.4%, faster than 2.5%, recorded in Q1’2019. The cost of funds, however, declined coming in at a weighted average of 3.1% in Q1’2020 down from 3.5% in Q1’2019 owing to the faster 12.2% growth average interest-bearing liabilities indicating that the listed banks were able to mobilize cheaper deposits,
- Average loan growth came in at 14.1%, which was faster than the 7.7% recorded in Q1’2019, with the growth in loans being accelerated following the repeal of interest rate cap in November 2019, coupled with increased demand in funding, as businesses demand working capital to operate in the tough operating environment as a result of the pandemic. As of May 2020, the key sectors that had received funding by banks were tourism and hospitality sector, transport and communication sector, trade sector, real estate sector, and the manufacturing sector which received 34.5%, 13.8%, 12.4%, 12.4%, and 11.8% respectively of the total funding by banks. Government securities, on the other hand, recorded a growth of 14.9% y/y, which was faster compared to the loans, albeit slower than the 16.1% growth recorded in Q1’2019. This highlights banks’ continued preference towards investing in government securities, which offer better risk-adjusted returns,
- Interest income rose by 8.2%, compared to a growth of 3.6% recorded in Q1’2019. The faster growth in interest income may be attributable to the 14.1% growth in loans and increased allocation to government securities. The net interest income increased by 7.4% slower than the 10.7% rise in average interest-earning assets. Consequently, the Net Interest Margin (NIM) declined to 7.2%, compared to the 8.0% recorded in Q1’2019 for the whole listed banking sector, and,
- Non-Funded Income grew by 15.9% y/y, faster than 10.7% recorded in Q1’2019. The growth in NFI was supported by the 24.5% average increase in total fee and commission income, which was faster than the 11.2% growth recorded in Q1’2019.
Section III: Outlook on the Focus Areas of the Banking Sector Players Going Forward:
In summary, the banking sector showed resilient performance despite the tough operating environment which was largely attributable to persistent revenue diversification evidenced by the 15.9% growth in NFI in Q1’2020 from 10.7% growth in Q1’2020. Growth in NFI was attributable to the growth in fees and commissions which recorded a 24.5% growth in Q1’2020. Despite this, core earnings per share declined in Q1’2020 by 7.4% as compared to the 12.2% growth witnessed in Q1’2019 pointing towards depressed earnings.
Based on the current tough operating environment, we believe 2020 performance in the banking sector will be shaped by the following key factors
i. Reduction of the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) during their 29th April 2020 meeting lowered the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR), which is a fraction of total customer deposits that the commercial banks have to hold with the Central Bank, by 100 bps to 4.25% from 5.25%. The reduction is projected to have injected approximately Kshs. 35.0 bn in additional liquidity, to commercial banks for onward lending to distressed borrowers. The reduction was a first one since July 2009. In their May 7th, 2020 presentation to the Senate Ad Hoc Committee on the COVID-19 situation, the CBK disclosed that 18 commercial banks and 2 microfinance banks had been granted approval to access Kshs 29.1 bn (82.6% of the Kshs 35.2 bn), following the CRR reduction. For more information on the funding allocation by sector in May compared to April 2020 see Cytonn Weekly # 21/2020,
Some of the listed banks that have provided the credit facilities include;
- KCB Group, which announced that it had set aside a Kshs 30.0 bn credit facility, in an effort to cushion individuals and businesses grappling with the effects of the Coronavirus pandemic. The credit facility will be accessed through the lender's mobile lending platform, KCB M-Pesa, and will issue loans from Kshs 50.0 to Kshs 1.0 mn, depending on the customer’s credit rating. The loan facility offers repayment periods of 30-days, 60-days, and 90-days with interest rates of between 2.0% and 6.0%, per month,
- Diamond Trust Bank (DTB), which committed Kshs.100 mn towards cushioning Kenyans against the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. DTBK will channel Kshs 50.0 mn directly to the COVID-19 Emergency Response Fund towards interventions for providing relief for the vulnerable families of the Kenyan Society. The other Kshs 50.0 mn will be used towards various supportive initiatives that the Bank would want to be involved in to support vulnerable members of the community, and,
- Standard Chartered Bank, which donated Kshs 122.0 mn to boost short term emergency relief to support vulnerable communities in the country. The bank has also extended Kshs 1.6 bn of additional financing to Small and Medium Entreprises (SMEs).
ii. Depressed Interest Income: With the large amount of restructuring and reclassification of loans witnessed in Q1’2020, we expect risks to crystallize in the next quarter given that the first Coronavirus case was reported in the country on 13th March 2020, just two weeks to the end of Q1’2020. Due to loan restructuring and relaxed rules on some interest payment, the bank’s core source of revenue which is interest income may be negatively affected. Banks are also not lending aggressively with the credit risk being relatively elevated with many sectors having been affected by the pandemic. We foresee a slower growth in loans in the next quarter and thereafter if the pandemic is to persist further with banks turning to less risky investments such as government securities which rose by 14.9 % faster than the 14.1% rise in loans in Q1’2020,
iii. Increased Provisioning- The risk of loan defaults remain elevated following the Coronavirus pandemic that has affected many businesses globally due to disruption in the supply chain and reduced demand due to constrained cash flows. As such, we expect higher provisioning requirements as per the IFRS guidelines, thus subdued profitability during the year across the banking sector, which is expected to be further heightened by the slow business activity in the country. As per the Stanbic Bank’s Monthly Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI), the PMI index came in at 37.5, 34.8, and 36.7 for the month of March, April, and May 2020, respectively, lower than the 5-year average of 51.4. A reading below 50 indicates a worsening outlook.
iv. Cost Rationalization: Given the expectation of depressed revenues, banks are expected to continue pursuing their cost rationalization strategies. A majority of banks have been riding on the digital revolution wave to improve their operational efficiency. Increased adoption of alternative channels of transactions such as mobile, internet, and agency banking, has led to increased transactions carried out via alternative channels and out of bank branches, which have been reduced to handling high-value transactions and other services such as advisory. Thus banks reduced front-office operations, thereby cutting the number of staff required and by extension, reducing operating expenses and hence, improving operational efficiency,
v. Continued Revenue Diversification - The increase in NFI growth outperformed that of interest income, thus, allowing the banks to remain profitable amid a rigid regulatory environment. However, with the new regulations put in place by the Central bank to cushion citizens against the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, banks’ non-interest income is likely to be depressed. Some measures such as waiving all charges for balance inquiry through digital platforms will see banks record lower income from the fees they charge,
vi. Expansion and Further Consolidation - With the Microfinance-Bill 2019 of increasing the minimum on core capital requirements still in its pilot stage more mergers and acquisitions would enable the unprofitable and/or smaller banks to manage the requirement and be able to increase profitability through cost efficiency and deposits growth.
Section IV: Brief Summary and Ranking of the Listed Banks based on the Outcome of Our Analysis:
As per our analysis on the banking sector from a franchise value and a future growth opportunity perspective, we carried out a comprehensive ranking of the listed banks. For the franchise value ranking, we included the earnings and growth metrics as well as the operating metrics shown in the table below in order to carry out a comprehensive review of the banks:
|
Bank |
Loans to Deposits Ratio |
Cost to Income Ratio |
Return on Average Capital Employed |
Deposit/Branch |
Gross NPL Ratio |
NPL Coverage |
Tangible Common Ratio |
Non-Funded Income/Revenue |
|
I&M Holdings |
76.0% |
52.9% |
17.5% |
3.6 |
11.3% |
58.8% |
16.3% |
38.8% |
|
DTB Kenya |
73.8% |
52.9% |
12.6% |
2.0 |
8.0% |
42.4% |
15.6% |
25.4% |
|
KCB Group Plc |
74.8% |
61.1% |
20.0% |
2.2 |
11.1% |
61.3% |
13.7% |
34.4% |
|
Stanbic Bank |
79.8% |
59.0% |
14.1% |
7.8 |
12.1% |
59.3% |
13.0% |
43.2% |
|
Co-operative Bank |
81.3% |
58.1% |
18.5% |
2.1 |
10.8% |
54.8% |
16.9% |
39.9% |
|
Standard Chartered Bank |
51.5% |
58.1% |
15.8% |
6.8 |
14.2% |
78.1% |
15.1% |
32.1% |
|
Equity Group Holdings |
75.9% |
64.7% |
20.7% |
1.7 |
11.2% |
45.8% |
15.7% |
41.9% |
|
NCBA Group Plc |
63.0% |
76.1% |
10.7% |
4.8 |
14.5% |
54.5% |
12.3% |
49.7% |
|
Absa Bank Kenya |
85.0% |
60.1% |
17.0% |
2.8 |
8.1% |
64.5% |
11.0% |
34.5% |
|
HF Group Plc |
101.1% |
101.1% |
0.5% |
1.8 |
27.3% |
52.2% |
16.8% |
30.4% |
|
Weighted Average Q1'2020 |
74.2% |
61.4% |
17.8% |
3.2 |
11.3% |
57.4% |
14.5% |
38.2% |
The overall ranking was based on a weighted average ranking of Franchise value (accounting for 40%) and intrinsic value (accounting for 60%). The Intrinsic Valuation is computed through a combination of valuation techniques, with a weighting of 40.0% on Discounted Cash-flow Methods, 35.0% on Residual Income and 25.0% on Relative Valuation, while the Franchise ranking is based on banks operating metrics, meant to assess efficiency, asset quality, diversification, and profitability, among other metrics. The overall Q1’2020 ranking is as shown in the table below:
|
Bank |
Franchise Value Score |
Intrinsic Value Score |
Weighted Score |
Q1'2020 Rank |
FY'2019 Ranking |
|
I&M Holdings |
51 |
2 |
21.6 |
1 |
2 |
|
Co-operative Bank of Kenya Ltd |
49 |
4 |
22 |
2 |
3 |
|
KCB Group Plc |
56 |
3 |
24.2 |
3 |
1 |
|
Equity Group Holdings Ltd |
60 |
5 |
27 |
4 |
4 |
|
DTBK |
67 |
1 |
27.4 |
5 |
5 |
|
ABSA |
62 |
8 |
29.6 |
6 |
7 |
|
Stanbic Bank/Holdings |
65 |
6 |
29.6 |
7 |
6 |
|
SCBK |
75 |
9 |
35.4 |
8 |
9 |
|
NCBA Group Plc |
83 |
7 |
37.4 |
9 |
8 |
|
HF Group Plc |
92 |
10 |
42.8 |
10 |
10 |
Major Changes from the Q1’2020 Ranking are:
- Co-operative Bank of Kenya Ltd whose rank improved to Position 2 from Position 3 in FY’2019 mainly due to an improvement in the Gross NPL ratio to 10.8% in Q1’2020 from 11.2% in FY’2019, in turn, improving its franchise value score, and,
- KCB Group whose rank declined to Position 3 from Position 1 in FY’2019 mainly due to a deterioration in the cost to income ratio to 61.1% in Q1’2020 from 56.2% in FY’2019 thus, in turn, worsening the franchise value score.
For more information, see our Cytonn Q1’2020 Listed Banking Sector Review
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this publication are those of the writers where particulars are not warranted. This publication is meant for general information only and is not a warranty, representation, advice, or solicitation of any nature. Readers are advised in all circumstances to seek the advice of a registered investment advisor.

